Common industry Fire Hazards
- SFE Services
- Oct 7, 2021
- 4 min read
Industrial fires can amount to a lot of cost for companies. Massive expenses per year, not even counting the loss of life that occurs. Disasters like this can happen because of numerous reasons, including the fact that a lot of employees and even managers are not aware of the many risks that surround them in the work place each day.
People have to be educated about our environment and fire in general so that changes can be made to prevent hazardous situations and create more safe spaces. Even the most basic of elements in an industry may not be permitted to become vulnerable and cause dangerous problems. For instance, rubbish and combustibles. This is why any building site should always be kept clean.
Here are some of the most common causes of explosions and industrial fires:
There is always a potential for fire in an environment where a heat source is found in a space together with flammable materials. A lot of industrial sites store very volatile materials that have the potential to explode or combust into flames when not stored or governed correctly. Here we will discuss only the general hazards, as every building and working environment are exposed to unique threatening situations that should be managed.
All employees and workers should be made aware and educated on the possibility of these varying fire emergency situations.
1. Combustible dust.
2. Flammable liquids and gasses.
3. Machinery equipment (hot work).
4. Electrical hazards.
Combustible dust:
Highly deadly, combustible dust is a big common cause of fire breakouts in woodworking, metalwork, pharmaceuticals, food- and chemical manufacturing, only to name a few.

Considering that it’s often overlooked calls for major concern in the general awareness of this type of substance. Just about anything in dust form can possibly be combustible.
These types of explosions are not generally easy to contain. A small dust explosion can result in dust in the area to rise in the air and possibly ignite causing another explosion. This second explosion can be much larger and more damaging, even to the extent that it could result in the coming down of the whole facility or building.
Prevention
The main thing that one can and should do is to primarily make sure that the dust doesn’t accumulate in large amounts. This is probably the first and best thing to make sure of to prevent this type of huge emergency accident.
Flammable liquids and gasses:

Usually occurring at chemical plants and can also be extremely tragic when misused. These types of liquids include; acrylic acid, crude oil and rocket fuel (that produces flammable gas). Flammable liquids require careful control. There are allowable limits for the amounts of these liquids permitted within buildings. Employees need to be aware and familiar with these limits as well as the proper storage thereof.
Flammable liquids;
These liquids can ignite with the smallest spark and are under no circumstances allowed to be in a boiler room or any environment where ignition can take place. When used, they must be handled with extreme care and stored in proper safety units/cans/cabinets/storage rooms. All being well designed for its purpose and according to the correct safety codes.
Compressed gasses;
Gases are not in themselves dangerous, it is the way that they are used that can result in gas being hazardous. When not used correctly it may as well result in a big accident. The primary concern are the chemical properties of the gases. This dictates the gas’s ability to react chemically with other materials. Causing hazardous quantities of heat or other reaction products.
Prevention
All available safety precautions should be implemented to eliminate these risks. Here are the general principles for controlling fire hazards associated with flammable gases and liquids.
· Store flammable liquids properly.
· Know the hazards.
· Control all ignition sources.
· Provide protective equipment.
Machinery equipment (hot work);
One of the major and leading causes of industrial fires are faulty equipment and machinery.

Heating/hotwork are usually the problems here. Like furnaces that are not installed correctly, managed, used and maintained. Also usually equated with welding and torch cutting, burning, blazing and smouldering. The sparks of these moulted materials reach dangerously high temperatures. Any work that results in these types of sparks or slag should be isolated away from hazardous materials.
Though any mechanical equipment can become a fire hazard due to the friction within a machine’s moving parts. But proper recommended cleaning, lubrication and maintenance can reduce these potential risks.
Prevention
Prevention strategies for any hotwork, faulty equipment and machinery issues that may result in a fire emergency.
· Awareness.
· Maintenance.
· Keeping a clean environment.
· Train personnel.
· Have personnel Wear fire-resistant protective clothing.
· Ensure that the area is clear of flammable or combustible materials.
· Supervise working areas.
· Use a written permit system.
· Install fire-resistant flooring.
· Protect doors and windows with fireproof curtains.
Electrical hazards
One of the top five causes of fires in manufacturing plants. The correct code requirements
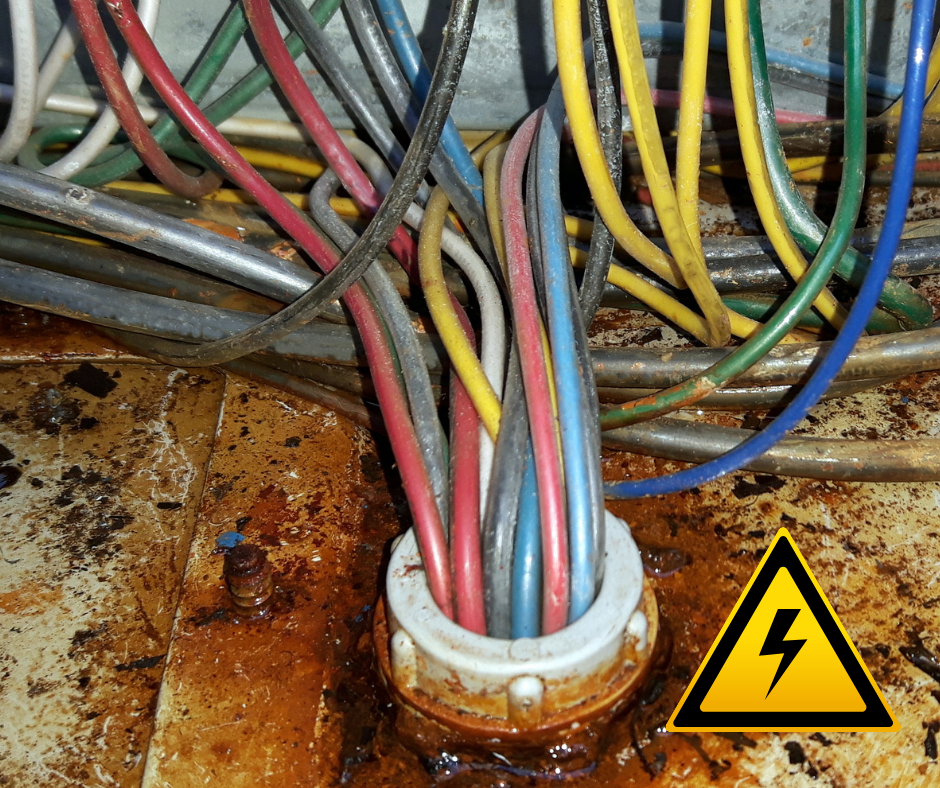
for proper explosive-proof equipment, wires and fixtures should always be followed. Any defective wiring and worn-out/dirty equipment are not to be allowed.
Instances that may occur (to be aware of);
· Wiring that is exposed.
· Worn extension cords.
· Overloaded outlets.
· Broken power tools.
· Greasy or dusty electric motors/machines.
· Static discharge.
· Overloaded circuits.
These electrical services are present in almost all structures. From the most basic appliances like microwaves and toasters to larger industrial electrical systems and machines. Although if these electric systems are all well designed, correctly installed and maintained properly, they can be safe and very convenient in the working place.
Prevention
An interrupted electrical circuit, carrying a current, can result of heating or arcing. This should always be taken into consideration, and the correct fire protection standards should be implemented as an attempt to prevent it.
Minimizing the risks will involve training, following the best sought out methods and maintenance;
· Don’t leave equipment for temporary use plugged in longer as needed (in use).
· Never overload the electrical circuits/equipment.
· If possible, avoid using extension cords (don’t consider it for permanent use at all).
· Regular cleaning of the working environment to clear any hazardous materials from areas that hold electrical equipment/machinery.
· Where required, use antistatic equipment.
· Implement a fire risk reporting system.
SFE Services specialise in the service, maintenance, supply and monitoring
of your Fire Safety Equipment and Smoke Ventilation. Make sure to contact us for your FREE survey.
#FlammableLiquidsandGasses #SFEServices





Comments